In Chemical Process Industries process safety is of utmost importance. And, to address this a process engineer analyzes all the possible scenarios during plant designing. Any wrong design may lead to a possible plant accident. As a single big accident such as toxic gas leakage, plant fire or storage tank explosion can do irreversible damage to the business. Moreover, it can be a big damage to the company’s brand and reputation. Therefore, to avoid accidents in chemical plants we need to look for safer design. Apart from this, we must do process safety analysis to identify any possible risk during plant operation. Hence, we must provide adequate safety devices such as instrumentation & controls, safety valve, rupture disc, flame arrestors and hazardous material handling equipment, etc.
In this article I will discuss about the pressure safety valve and its specification sheet. The pressure relief valve (PRV) could also be referred to as a pressure safety valve (PSV) and relief valve. Any system operating at pressure such as vessels, reactors or tanks requires safety devices. These safety devices are mainly safety valves or rupture disc which can protect plant, people & process. We can define a safety valve as a safety device, which automatically open, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned. And, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded. Moreover, which is designed to re-close automatically and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored.
Table of Contents
Design of Safety Valve
Below is the figure, which you can refer to understand the design of a typical safety valve:
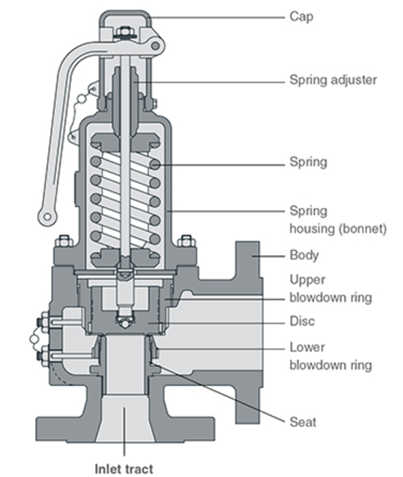
In below specification sheet you can provide various data & information for the supply of a suitable safety valve. Below is the format for PSV specification for your reference.

In above specification sheet you can provide various data for the required pressure safety valve (PSV). It has various sections in which you can provide details like General, Connection (here we provide size & rating for inlet/outlet connections). In Material section we provide the materials of construction for the various parts of the safety valve. We can provide the details for design Code and design basis (i.e., for blocked flow or fire case) in Basis section. Fluid properties we can provide in Fluid Data section. While Other Data section contains that information which pressure safety valve supplier will be provide based on selected and designed PSV.
Safety Valve Sizing
A process engineer needs to provide the sizing data to the safety valve supplier, so that based on that vendor can design or select an appropriate pressure safety valve. To understand this safety valve sizing exercise, we will take an example of pressurized vessel containing ammonia. Below are the details for the storage vessel:
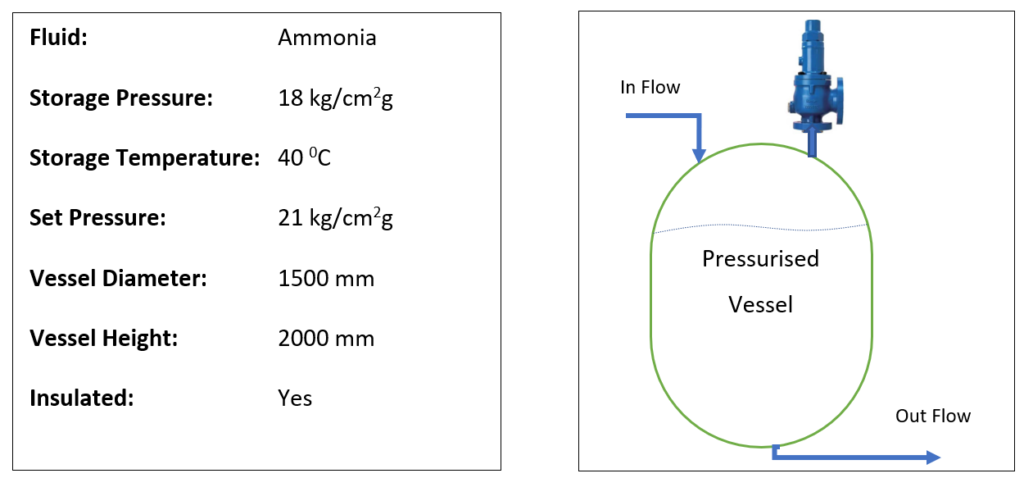
To estimate the capacity for safety valve we can look in two ways, first is blocked flow case and second is fire case. Blocked flow means when in-flow is ON inside a pressure vessel and out-flow is blocked. In that case the pressure inside the vessel will keep on increasing. So, to release the excess pressure in blocked flow condition required release capacity will be equal to the in-flow rate of the stream.
Second, for fire case when there is fire surrounding the vessel. Then, there will be heat ingress into the vessel through the surface and liquid inside the vessel start boiling and pressure start increasing inside the vessel. In this case to restore the vessel pressure, relief valve releases the excess vapour generating because of rate of heat ingress during fire.
So, after looking for both the cases which ever flow is higher between blocked flow and fire case, we consider that as capacity for the pressure relief valve.
Flow Capacity Estimation in case of External Fire
Below formula you can use to estimate heat inflow rate during external fire. After estimating heat input rate dividing it by latent heat of vaporization of the fluid you can estimate mass flow rate of vapour generation.

Safety valve release capacity for fire case = Q / Latent Heat of Vaporization
So, first you get the mass flow rate for both the condition (i.e., input mass flow rate and second mass flow rate for external fire). Between these two mass flow rates, whichever mass flow rate is higher, we consider it as design mass flow rate for the relief valve. This data we know as require capacity (kg/h) for the pressure relief valve.
Types of Pressure Safety Valve
We can find mainly below types of PSV or PRV in our plants:
Balanced Pressure Safety Valves
When back pressure is > 10% of the set pressure at 10% allowable overpressure, we should use balanced pressure relief valves. Because a conventional PRV shows unsatisfactory performance when excessive back pressure develops during relief of excess fluid. This excess pressure builds up due to the fluid flow though the valve and outlet piping. Therefore, to handle this issue, we use a balanced pressure relief valve to decrease the backpressure effects. Simultaneously it protects the bonnet spring and guide from released fluids in case of corrosive fluid services.
Conventional Spring Loaded
We can use a conventional spring loaded PRV, where built up back pressure is <10% of the set pressure at 10% allowable overpressure. In addition to this, these PRVs are suitable for non-corrosive services as well. Conventional spring-loaded valves consist of the bonnet, guide, and spring in the released fluids. As the bonnet vents into the atmosphere, the relief-system back pressure lowers the set pressure. However, as the bonnet vents inward to the outlet, the process is reversed and the relief-system backpressure makes the set pressure higher.
Pilot Operated Safety Valve
This type of PSV is a self-contained system. And, these type of safety devices does not require any external power or pressure source to operate it. Here, the operation of safety device is initiated and controlled by the fluid discharged from a connected pilot valve. This pilot valve is a direct spring-loaded safety valve designed for the required pressure conditions.
Conclusion
So, I guess you can prepare specifications for a safety valve using this article. Also, to download the specification sheet format for your help please click here. Also, please note a safety valve is useful when pressure increase in a system is gradual. Which is the scenario in case of in blocked flow or external fire case. While, wherever there are chances of explosion or reaction run away. We need to provide a rupture disc to release the sudden pressure rise. Because a rupture disc can burst at a set pressure immediately to release the pressure immediately to protect the equipment.
Finally, always we should first look for a safer design. And, subsequently provide adequate safety devices to protect the people, process & plant.
Thanks for reading..
