Pumps are just like a heart of any chemical plant, which are continuously running for feeding, circulating or transferring fluid from one point to another point inside a plant. For trouble free operation, appropriate selection of pumps is very important. For this you need to know the nature and characteristics of the service fluid . Type and size of the Pump is decided base on the various process requirements. This we summarize in a pump process data sheet.
Table of Contents
Parameters required for selection of pumps are such as
- Capacity of pump (m3/h)
- Required discharge head (meter)
- Fluid Viscosity (cP)
- Fluid density (kg/m3)
- Suspended Solid Content in pumping fluid (wt%)
- Vapour pressure of fluid (kPa)
- Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH available in meters)
- Working temperature (0C)
- Working pressure (kg/cm2g)
- Corrosion compatibility of pumping fluid
- Hazardous class for pumping fluid
- Based on the above information required pump can be designed which includes
Design of pump includes as below
- Type of pump (Centrifugal/Reciprocating/Diaphragm, etc.)
- Pump model selection
- Power calculation and motor size selection
- Material of Construction for pump
- Seal type and it’s flushing plan (mechanical or gland pack)
Common type of pumps used in industry
There are two major type of pumps in chemical industry. First Centrifugal Pumps and Second Positive-Displacement Pumps. The Positive-Displacement Pumps further divided in two sub-classes as Reciprocating Pumps and Rotary Pumps.
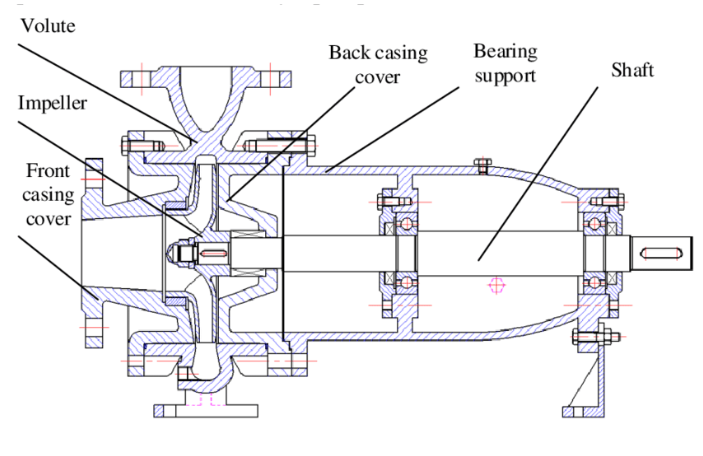
Centrifugal Pump
In this pump centrifugal action convert mechanical energy into pressure energy which is the gradient for fluid flow. The major parts of centrifugal pump include high speed rotating impeller (rotating at 1450 or 2900 rpm commonly). Casing or housing of pump where impeller rotates, impeller shaft, stuffing box and seal to prevent leakage between shaft and casing gap.
This is the most commonly used pump in chemical industry. This pump is useful where we need high pumping capacity and lower discharge head. However, for high discharge pressure requirements, we can use multistage centrifugal pump. These type of pumps delivers fluid at a uniform pressure without shocks or pulsations. Moreover, centrifugal pumps can handle a wide variety of corrosive fluids and slurry, as we can provide anti-corrosive/anti-abrasive coating on pump casing and impeller.
Positive-Dispacement Pumps
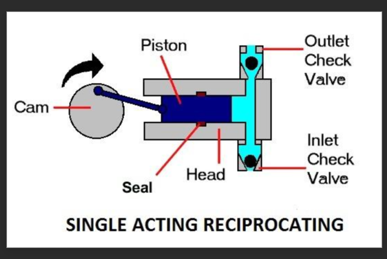
These pumps cater to service where we need to transfer fixed amount of liquid regardless of upstream pressure level. Positive-displacement pumps are favorable comparatively to the centrifugal pumps, where low volume of fluid is pumped at high discharge pressure. However, these pumps require comparatively higher maintenance cost.
Reciprocating pumps examples includes piston pumps, diaphragm pumps and plunger pumps. Commercially available piston pumps can pump upto 50 atm discharge pressure. Plunger pumps can pump against more than 1500 atm discharge pressure. Diaphragm pumps are suitable to handle corrosive and toxic fluids and can pump small amount of fluid (i.e., around 100 gal/min) and can develop pressure more than 100 atm.
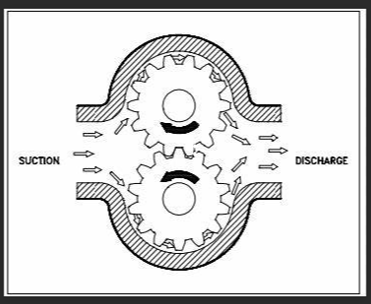
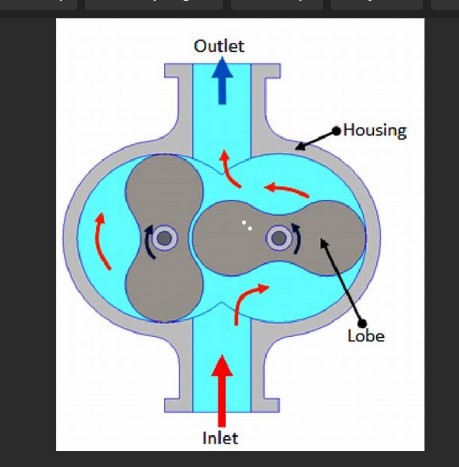
Other sub-class of positive-displacement pump is Rotary Pumps, various type of example for rotary pumps are such as lobe pumps, gear pumps, screw pumps and vane type pumps. These type of pumps are conducive to pump highly viscous fluids like polymers, pastes, solid slurry, etc.
Efficiency of Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are most efficient and their operating efficiencies can be in the range of 70 – 90% as they have lesser friction losses and other leakages. While in case of reciprocating pumps operating efficiencies can be in the range between 40 – 75%.
Challenges in Pumping
Abrasive Fluid
Liquid containing abrasive suspended solids inside pump can cause severe damage on the impeller and inside of the casing. Therefore, in this case during selection of pumps you should consider below points.
To resolve this problem we can use hard material of construction or wear resistant lining on abrasion prone impeller and inside of casing.
Rubber lining has the ability to absorb the shock energy of abrasive particles and provide safety from damaging pump internals. When pump is operating under vacuum use of rubber lining is not recommended. Other limitation for the use of rubber lining is the temperature more than 100 0C and the presence of organic.
For handling low flow rates diaphragm pumps are also best option. Like other all reciprocating pumps, diaphragm pumps do not have seals.
Liquid Solidify
In our plant we handle the situation where liquid solidifies inside the pump. This causes breakdown and leads to shutdown the plant and therefore need to take up the de-choking activity of pump. Moreover, the nature of solidification varies with the fluid we handle and all these things makes selection of pumps very tricky.
High melting point of the fluid like heavy hydrocarbons. For pumping such fluid it is required to maintain the temperature of the system above melting point of the fluid. To avoid this problem, provision of pump jacket is a good solution. Wherever, providing jacket it not possible, we must flush the pump completely when pump is stopped or in standby condition.
Crystallizing Fluid
Crystallizing liquid causes damage to the pump shaft seal. Situation become worse, the crystals can cause rubbing contact between the shaft and the stationary seal face. This results in fracture of seal face. Therefore, to avoid this problem, there should be provision for continuous removal of the crystal deposits by washed away with an inert fluid.
Polymerizing Fluids
Many liquids undergo polymerization during pumping, which is prominent in stagnant zone of the pump. In such situations use of open impeller can be one solution. In some cases when pump is left under standby condition, draining provision can be the wonderful solution.
Highly Corrosive Fluids
Highly corrosive liquid (like H2SO4, HCl, HNO3, etc) handling is also a common challenge for us in day to day plant life. Therefore, understanding fluid characteristics including pH, temperature, concentration and presence of contaminants are important. Moreover, change in these parameters severely alter the corrosion attack. For example, dilute H2SO4 is highly corrosive while pure H2SO4 in less.
The possible solution is to select the suitable corrosion-resistant alloys for pump manufacturing. Therefore, material of construction SS316L is most frequently used it contains 18% chromium, 8% nickel and 3% molybdenum.
However, use of non-metallic pumps made of Glass-lined, PVDF, PP-FRP, HDPE and PP are also good options in these services.
Fluids with Two Phase
Two phase flow pumping involves having undissolved gases and vapours. For example, fermentation wash in distillery, where molasses is fermented using yeast and it produces ethanol and CO2. The fermenter circulation pump contains liquid and gas in this case. Therefore, presence of gas or vapour affects the performance of pump and can stop the pumping of fluid completely. Self-priming pump which will evacuates all the entrained gas, can be the solution for this problem. However, use of positive displacement pumps is also a good alternative in these type of situations.
Viscous Fluids
Pumping highly viscous fluids like pastes, plastic polymers, and molasses is a unique challenge. In such services viscosity plays an important role for pump selection. Because high resistance to flow implies a higher system resistance. Therefore, screw or rotary pumps with large size piping for suction and discharge is the suitable solution for this situation.
Hazardous Fluids
For handling hazardous fluid, which are toxic, flammable & dangerous. Today’s strict compliance requirements don’t allow leakages of such fluids into the environment. This leakage is very harmful for the environment and can cause major accidents inside the plant.
The solution to this problem is slightly costly like use of seal-less pumps, provision of double mechanical seal.
Conditioning monitoring of the pumping system is also a good solution, providing sensors for temperature, pressure and leak detection sensors will give inputs to activate emergency shutdown controls. This will contain the fluid emission.
Hence, you can see selection of pumps is very important to meet the specific pumping requirement. Any error in specification will lead to the wrong selection of pumps and will cause for frequent breakdowns and inefficient operation.
Thanks for reading and looking forward for your valuable feed back.


Thank you, K Mehra, for writing such an informative guide on choosing the right pump. Diaphragm pumps are used for a wide range of hazardous-liquid handling applications because they lack mechanical seals and packing and are essentially sealless.
Thank you…