As a chemical engineer we are involved in number of small or big projects. Where we initiate the project and perform number of activities, to meet end results within a pre-defined time frame. In our plants, these small projects can be like, plant maintenance activities, equipment replacement work, running a product campaign, plant performance improvement initiatives, etc. On other side there can be large projects, such as new plant project, existing plant debottlenecking and revamping, new ERP implementation, plant digital transformation project, new product development, etc.
We can see in all above projects there are large number of activities involved from start to finish. Simultaneously, cross functional team members are also there. So, for timely completion of our project we need effective management of these activities. Moreover, efficient coordination among all stakeholders is very critical. Therefore, for a chemical engineer it is very necessary to understand the project management fundamentals to handle any project successfully.
This is my first article in the series of “Understanding of Project Management Fundamentals”. And, in subsequent articles we will go through in details.
Table of Contents
What is a Project?
So, let us understand first what is a project. We can define a project is a series of activities which are temporary and we perform these activities to create a unique product or service. Hence, we can say,
- Each project has a certain time bound goal.
- Has numbers of activities which we need to complete timely (i.e., has start and finish date). For this we use Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) method to get insight in quantum of the project work.
- Require resources (Man, Machine and Material) to carryout different activities.
- These activities are temporary, which are not require after project completion.
- Each project has a unique output which can be a product such as a manufacturing plant, product, school building, etc. Project for services can be like ERP system implementation, digital transformation of plants, plant shutdown activities, etc.
We can see project is a process, where a series of actions takes place to bring about desired results. So, we can divide whole project activities in five different process groups or phases as below:
- Initiating
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring & Controlling
- Closing
In subsequent section we will discuss about these process groups in detail.
Difference between Project v/s Operation
Now many times we are confused between project and operation. You should be clear in your mind operation is different than project. Below are the points which will clarify your doubts:
- A project has its unique charter, organization and specific goal. While, in operation you have a permanent charter or SOP (standard operating procedure) and fixed goals (like to meet daily production, consumption norms).
- Every project after completion delivers a unique product or services. While, operations are meant to deliver same thing regularly and repetitively.
- In projects we can see team members are from diverse fields and specialization like chemical, civil, architect, mechanical, electrical, instruments, painter, welder, project manager, safety person, etc. On other side in operations, we have more homogeneous teams where you require less expertise. Such as plant operation people, maintenance technicians, etc.
- A project is time bound activity and has a start and end date. While, operation is an ongoing process, which stops only during maintenance and breakdown events.
Now, we have understood about project and also the difference between project and operation. Let us move to understand about managing the project.
Project Management and Manager
Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities. This is required to meet the stakeholders needs and expectations from that project. These stakeholders can be investors, business head, plant head, customer, supplier, community, local government, environment bodies, etc. And the person who is responsible for managing a project is known as Project Manager.
So as a project manager you need to manage the five-process groups or phases activities as we discussed above. During this whole process you need to focus and integrate the project scope, time duration, project cost, product or service quality, avoidance of any risk, procurement, resource management areas. A project manager use communication as a mean to integrate all the project information.
Therefore, to manage a project systematically as project manager need to do below things:
Project Phases
Initiating – Define the project goal, scope, time, cost and team members with clear cut roles and responsibilities. In this phase actually we are setting the project’s baseline for time, cost and quality. For this purpose we prepare project charter, which includes all these information. It is always better to get signed-off the project charter from all the stakeholders before starting any project.
Planning – Identify best possible plan for activities and resources (including Man, Machine and Materials) among available options. This you need to achieve the objective or goal of your project.
Execute – This phase includes integration activities of a project manager in which he interacts among team members to implement the project plan.
Controlling – This is the regular activity which a project manager performs to measure and monitor the progress of his project. For this purpose, he uses variances for time, cost and quality of work from the set baseline. If progress is deviating from plan, then he takes corrective actions to meet the particular project phase and overall project goal.
Closing – This is the last phase of any project and project manager get the acceptance from stakeholders regarding the product or services. Here project manager submits a closing report including standard operating procedures, user manuals, performance certificates, training, etc.
Below figure is to show you the interaction and flow of information between process groups during project life cycle. The direction of arrows here represents the flow of information.
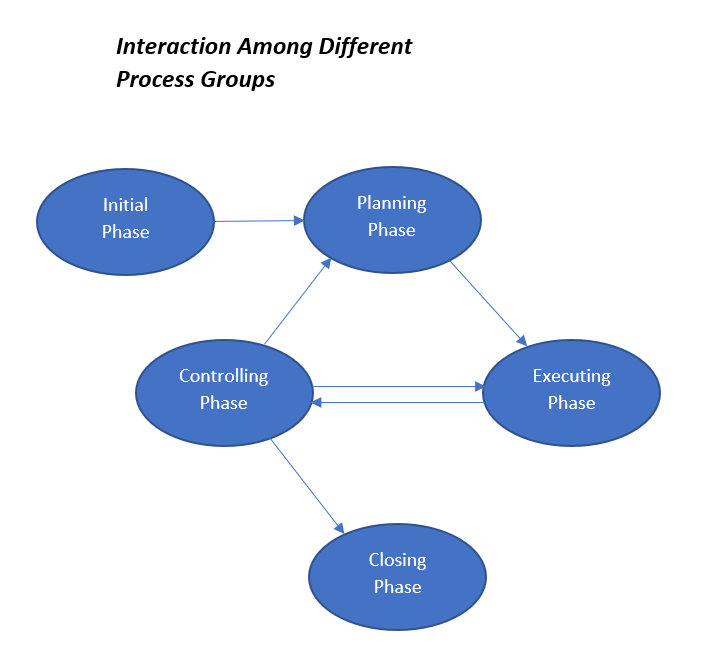
As a project manager, you are supposed to keep all stakeholders as happy as possible. There may be parties having conflicting interests also. So, to achieve this expectation you need to control the project and for controlling you require measurable parameters having planned limits or baseline parameters.
As we discussed above what is a project management and how a project manager control and manage a project. Simultaneously, as a project manager you must keep in mind common pitfalls which can lead your project to failure.
Common Hurdles in a Project
As we know, nothing is ideal in this world and we cannot assume a smooth road map for our project also. So, it is very critical to understand the possible pitfalls in our project process as follows:
- Many times, we take up a project without a clear goal or objective. This makes our plan vague and spread confusion among team members. Which will certainly fail our project.
- For smooth project progress senior management support is very important. Because you are dependent on them for providing financial support and policy decisions making. Any misalignment in this can stall or altogether force to drop the project.
- As a project manager, if you are not an effective and efficient communicator you will face many problems because of poor coordination. To integrate team members, activities, stakeholders, cost, quality and risk as a project manager communicate timely and clearly to the project team. Therefore, as project manager you should have good communication skills in all form of communication such as verbal, non-verbal and written.
- Sometimes, you start a project and in between business priorities changes. This will lead to drop the project altogether and retrofitting may be required. Which is a very problematic and painful process.
- Because of non-availability of money your project can be delayed or dropped.
- For the success of any project, it’s team members are very important. If in initial phase selected team member are not competent enough, this will impact your project adversely.
Project Life Cycle
As we discussed about project phases from start to end for a project. So, collectively these project phases namely Initial, Planning, Executing, Controlling and Closing, we know as the project life cycle. In a project phase we group the activities based on logics which on completion convert in a project milestone. Like after Initial phase we will be ready with our project charter, which is a very important milestone for the project. During the project life cycle flexibility and difficulties of various parameters like cost & effort, risk, influence, stake involved, stakeholders change with time. This you can by below figure:
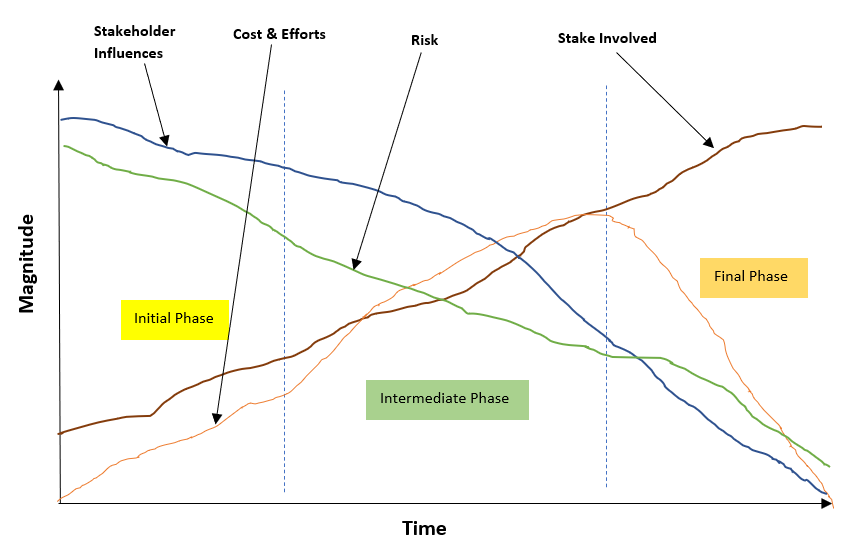
So, it is evident from above generic project life cycle figure as project time moves towards end, risk involved and stakeholder influences decreases. While, stake of stake holders involved increases in a project as project progresses. In case of project cost and efforts are in increasing trends from initial to intermediate project phases and subsequently it decreases in the final phase of the project.
Overlapping of Project Phases during Project Life Cycle
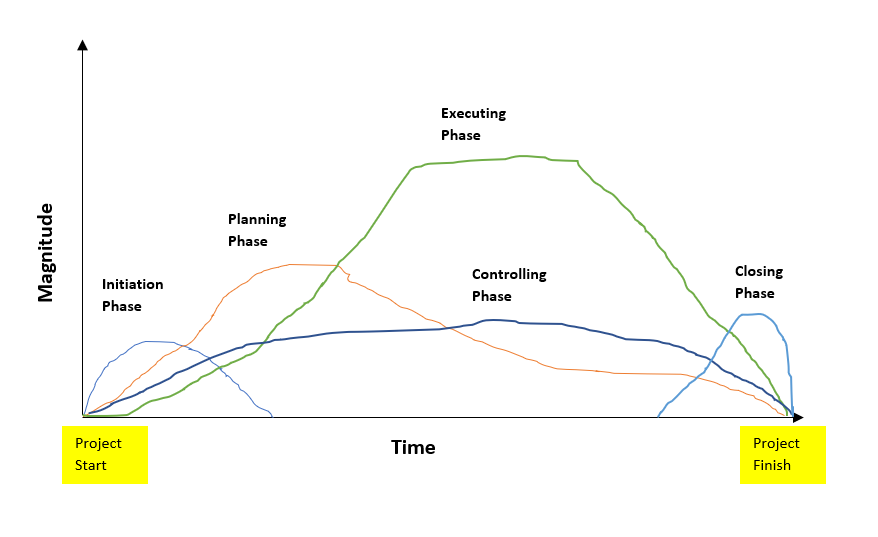
You can understand overlapping of project phases during project life cycle by below figure. Here we can see initial and closing phases are for small portion time activities of total project time. While other phase planning, execution and controlling phases are activities which you need to perform throughout the life cycle of a project. Among these three planning activities are higher during the initial part of the projects, while execution phase is on peak at towards end of the project life cycle.
PMO – Project Management Office
Generally, a project manager is responsible to manage a single project at a time. However, in case of small projects he can handle multiple projects also. So, at enterprise level where many numbers of large size projects are running, there you can see an organization to handle these big projects. This organizational structure with specific mandate & having enterprise perspective, we know as a PMO or Project Management Office.
The objective of PMO is to manage major program to achieve business objectives efficiently and economically. PMO control and manage resources (man, machine & material) across all the projects in an optimum way. Moreover, responsible to manage overall risk, opportunities and interdependencies across all the projects.
At enterprise level PMO collects reports from all the project managers working over different projects. Subsequently, PMO consolidates all the reports and presents to the board members. This helps in making decisions to divert and deploy shared resources in projects running behind the schedule.
Conclusion
In this article we got the introduction about project, project management, project manager and difference between project vs operation. Moreover, we discussed about various project phases and their importance. Subsequently, we saw the relationship of project progress time with various parameter like project cost, risk, influences and stakes involved. We also got introduction about project management offices or PMO.
Thanks for reading…

Very Informative Article on Project Management Office. So Highly Recommended to all who wants to build career in Project Management.
Thanks for your appreciation.